9F, Zhongrui Jumei Building, 68 Jiuzhang Road, Suzhou Industrial Park, Jiangsu Province
Overseas talents
How to ensure medical quality under DRG payment?
In 2021, DRG payment will enter a critical stage, and multiple pilot sites will enter the actual payment stage. Three years after the DRG trial, after breaking the rule of paying by project and by bed day, the "anxiety" still fills the minds of all departments in the hospital. Whether the anxiety in the medical insurance department is "losing money", and whether the "accuracy rate of the main diagnostic code" for medical record anxiety meets the standard, then the topic that doctors and medical personnel are most concerned about is whether "medical quality" can be truly guaranteed. Medical quality is fundamental to the long-term development of hospitals. Has the medical quality deteriorated or improved under DRG
DRG grouping process: clinical evidence-based validation again
The DRG grouping process does not appear to harm the quality of care. DRG starts from medical theory and focuses on data analysis. Each group strictly follows the hierarchical logic from anatomical systems, to disease treatment methods, to individual characteristics of medical records
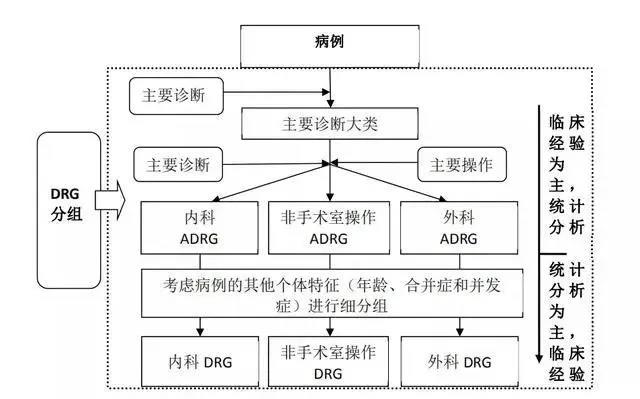
Figure 1 CHS-DRG grouping process
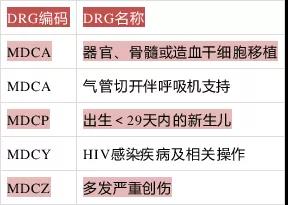
Before proceeding with the classification of major diagnostic categories (MDCs), first, based on the data on the front page of the medical record, organ transplants, ventilators who have been used for more than 96 hours, are aged less than 29 days, and are primarily diagnosed or otherwise diagnosed with HIV or severe trauma. They are divided into early groups to form MDCA, MDCP, MDCY, and MDCZ
Table 1 Table of Contents for Early Grouping
Example:
Main diagnosis: chronic kidney disease, stage 5 anemia
Main surgery and procedures: renal allograft
In this case, kidney transplantation is an organ transplant operation, and it is the first choice to enter advanced grouping, which does not take into account other factors such as the patient's age, gender, disease location, and so on. Therefore, they were divided into "AE1 renal transplantation" group
After preliminary grouping, the remaining cases are classified into different main diagnostic categories based on the main diagnosis on the front page of the medical record and the gender factors of the individual case (i.e., different MDCs; reproductive system diagnosis considerations require classification into MDCN or MDCM based on gender differences), and each MDC has a main diagnosis table. CHS-DRG is divided into a total of 26 major diagnostic categories (MDCs)
The main diagnosis and surgical procedures on the front page of the medical record are the key basis for classification into the core disease diagnosis related grouping (ADRG). That is, all cases undergoing surgery or manipulation in the operating room are divided into relevant surgery and manipulation groups, while others are divided into relevant medical case groups based on their main diagnosis. CHS-DRG was initially divided into 376 core disease diagnosis related groups (ADRGs), including 167 in the surgical group, 22 in the non surgical group, and 187 in the medical group
Combining other factors that affect the clinical process, such as individual factors of the case, the presence or absence of complications and complications, their severity, and the way of leaving the hospital, the final DRG group is generated. CHS-DRG was divided into 618 disease diagnosis related groups (DRGs)
Doctor behavior feedback under DRG
The grouping logic of DRG is derived from the home page. The influencing factors for grouping involve factors such as main diagnosis, main surgical procedures, complications, and serious complications. The DRG enrollment situation is almost linked to one another, causing a loss if one is careless. This also restricts doctors' behavior on the other hand, changing the previous game rules under "project based payment", and changing doctors' disorderly and excessive medical behaviors such as "relying on memoirs to supplement medical records", "relying on medication and examination to increase income". However, "The ideal is very plump, and the reality is very skinny." DRG is a double-edged sword. Although the grouping principle follows evidence-based medicine, in reality, under the prepaid system, in order to avoid the impact on hospital income, it is inevitable that it will lead to deviations in the behavior of clinicians, and generate some uncertain factors on the guarantee of medical quality. Relevant researchers have conducted research on this issue
In 2019, Peking University led a study on the medical quality of patients with acute myocardial infarction in Beijing and found that there were significant changes in the diagnosis and treatment behavior of DRG-PPS pilot hospitals, especially changes in medication behavior during diagnosis and treatment, which may affect the quality of the medical service delivery process
In particular, medical personnel from clinical departments such as pediatrics and critical care medicine are represented, and there are many concerns about the medical risks and ethical issues arising from the limitations of external payment standards and internal cost control requirements in the post-reform diagnosis and treatment operation process; In some reform areas, patients with stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and osteoarthrosis are not suitable for DRG-PPS payment due to the fact that the course of disease involves rehabilitation treatment in the late stage of acute treatment, resulting in forced early discharge or multiple hospital transfers. Similar situations not only affect the normal treatment process and medical experience of patients, but also have unexpected policy implications for the development of relevant specialties in medical institutions
Hu Guangyu from the Research Center for Health Policy and Management of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences believes that "from the perspective of institutional arrangements, medical insurance expense control is a rigid requirement for maintaining the safe operation of the fund. At the same time, it should be recognized that meeting the basic medical service needs of insured persons is equally important to achieving the goal of reforming the medical insurance payment method as ensuring the healthy and sustainable development of medical and health undertakings."

Measures to ensure medical quality under DRG payment
How to ensure the balance between medical quality and DRG fee control requires multiple measures to jointly ensure:
1. Implement clinical pathway management
China's health administration began implementing clinical pathway management as early as 2009, releasing more than 1000 clinical pathways, laying the foundation for standardizing clinical diagnosis and treatment behavior and ensuring medical quality. On January 2, 2020, the National Health Commission issued and interpreted the "Clinical Pathways for Related Diseases (2019 Edition)". This time, the National Health Commission organized the revision of clinical pathways related to disease types in 19 disciplines, forming 224 clinical pathways for disease types (2019 version) for clinical reference
Under clinical pathway management, treatment methods follow the first diagnosis without considering complications and complications. Using traditional clinical pathways to control the cost of DRG is obviously unrealistic. Clinical pathways require new thinking, and difference analysis based on big data is particularly important. Through big data analysis of medical records, comparative analysis of resources consumed by clinical pathways is conducted, and a profit and loss control group based on DRG profit and loss measurement is established to further implement a profitable DRG based clinical pathway
In response to the difficulty of promoting clinical pathways in the hospital, Wuhan First People's Hospital has done this in clinical pathway management: strengthen the implementation of clinical pathway management for common and frequently-occurring diseases, train clinicians to strictly follow the guiding principles of clinical pathways, standardize pathway management, and allow a certain withdrawal rate for some special cases in the event of emergencies
2. Third Party Supervision
Cai Liming, a senior economist in the actuarial department of the Center for Medical Insurance and Medical Assistance Services (CMS) of the United States, once said, "There are many experiences that China can learn from over the past 30 years of DRG operation in the United States, including the establishment of independent regulatory bodies to supervise hospitals' rejection of patients or rejection of referrals, insurance fraud, and other situations. The membership can be medical administration, medical management departments, and third parties, strictly monitoring the quality of hospital medical services."
Similar to the Recovery Audit Contractor (RAC) in the United States, this institution specializes in auditing and supervising hospitals and doctors; Within CMS, with the Obama healthcare reform policy, a Center for Program Integrity (CPI Program Integrity Center) was established, specifically responsible for coordinating and directly managing all Medicare anti fraud activities. The deep participation of these third-party institutions and a more transparent healthcare payment process can greatly reduce the negative impact mentioned above
Currently, the medical insurance flight inspection system implemented by China's medical insurance bureau only inspects medical insurance fraud. In terms of DRG and DIP pilot activities, no third-party regulatory agency has been established or clear policies or systems have been established to regulate relevant behaviors. According to the author's understanding, the medical insurance bureau currently has no practical punishment measures for violations such as high base code. However, in terms of the Health Commission, in the "Criteria for the Evaluation of Third Level Hospitals (2020 Edition)", provisions are made for the types of diseases with low risk group mortality and other indicators related to medical quality and safety, adding a "tight curse" to medical quality through multiple dimensions such as grade evaluation, performance evaluation of public hospitals, and pilot high-quality development of public hospitals
Finally, in a nutshell, doctors are the key to final implementation. What is the boundary of diagnosis and treatment norms under DRG, what is the focus of medical cost control, and whether to "control expenses" for the purpose of "controlling expenses"? This not only tests the wisdom of doctors, but also puts forward higher requirements for hospital management personnel and medical insurance parties

